Voice of sage of the ages echoes down the centuries
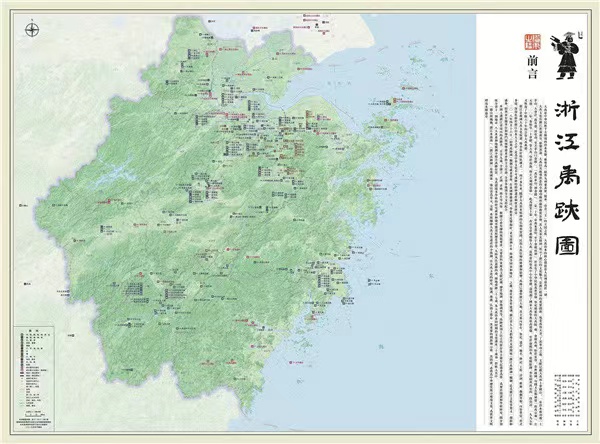
Zhejiang Yuji Tu (Map of Traces of Yu in Zhejiang province). [Photo provided to China Daily]
In China, Dayu, or Yu the Great, is a household name and a character who figures prominently in the origin of Chinese civilization. He is credited with establishing the Xia Dynasty (c. 21st century-16th century BC), the start of China's dynastic rule. Even some toddlers can vividly tell his heroics of controlling the primordial floods that had once ravaged the lands.
Indeed, it is often said in historical records that "Around the Nine Regions, traces of Yu can be found everywhere, and temples commemorating Yu can be seen everywhere". Nine Regions is a term generally found in ancient Chinese history referring to Chinese territories and has since taken on the meaning of China.
Now, with the publication of a map and its accompanying materials, including a book of copious notes and photos, a fuller picture of Yu's achievements is available, one that gives a deeper insight into his legacy.
The map, covering 26 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities, which is titled Zhongguo Yuji Tu (Map of Traces of Yu in China), documents 323 of more than 1,000 Yuji, or traces of Yu, across the country.
"It is by no means a simple list," says Qiu Zhirong, one of the chief editors of the map and deputy head of the Water History Committee of the Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society. "Rather, it is a serious academic exploration of a major Chinese historical and cultural phenomenon."
First, Yuji, or traces of Yu, have been clearly defined. They include sacrificial activities, memorial buildings, inscriptions, ruins, historical records of his stories and folk tales, as well as place names and a few movable relics and intangible cultural heritage, among others, that are based on Yu's flood control and have survived to this day, researchers who have compiled the map say.
"Each entry has been rigorously selected," Qiu says. "Many scholars have started to visit and conduct field investigation on the 'traces of Yu' since the early 1990s, and their research has laid a solid foundation for the publication of the current map."
Using the map and supporting documents, readers can readily pinpoint the location of each point of Yuji and find out its name, category, origin, current status and in which historical documents it was first recorded.
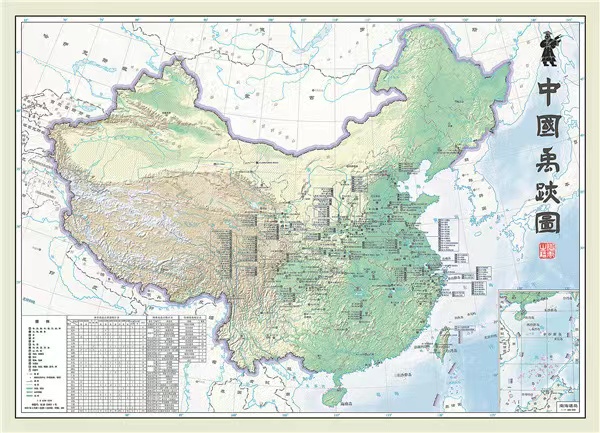
Map of Traces of Yu in China. [Photo provided to China Daily]
For a long time, Yu had been regarded by some as mythical, but more recent archaeological and historical findings have led to a revaluation of the historicity of him and his flood control. In the 1960s archaeological excavations at Erlitou in Yanshi, Henan province, an early Bronze Age site, turned up remains of palaces and ancestral temples that predated the Shang Dynasty (c. 16th century-11th century BC). The ruins of Wangchenggang, in Dengfeng, Henan province, excavated in the 1970s, are believed to be the capital established by Yu in about 2070 BC and recorded in pre-Qin (221-206 BC) literature.
Archaeological excavations have also confirmed that several regional civilizations existed along the Yellow River, the Huaihe River, as well as the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and the Taihu Plain between 10,000 and 4,000 years ago.
In fact, in the Song Dynasty (960-1279), an effort had already been made to draw the Yuji Tu (Map of Traces of Yu). The one that had been engraved on a stele in 1136, and that now resides in the Forest of Stone Steles Museum in Xi'an, Shaanxi province, is one of the earliest extant national maps and among the most famous.
The first attempts to make the current Zhongguo Yuji Tu were in 2017, when Qiu and his collaborators set out to compile the Shaoxing Yuji Tu (Map of Traces of Yu in the city of Shaoxing in Zhejiang province), which was published in 2018 and the following year was expanded to become the Zhejiang Yuji Tu (Map of Traces of Yu in Zhejiang province). It is no coincidence that Shaoxing was the focal point, for it was to this place that Qin Shihuang (259-210 BC), China's first emperor, traveled and performed sacrificial rituals for Yu the Great.
Shaoxing is also where Yu's mausoleum lies today and where the most widely heard story of his is said to have taken place.
It is said that when Yu the Great went about taming the floods, he met a member of a local clan and they married. However, a few days later Yu had to leave home to continue fighting the scourge of floods. For the next 13 years he did not set foot in his home again, even though he went by it three times.
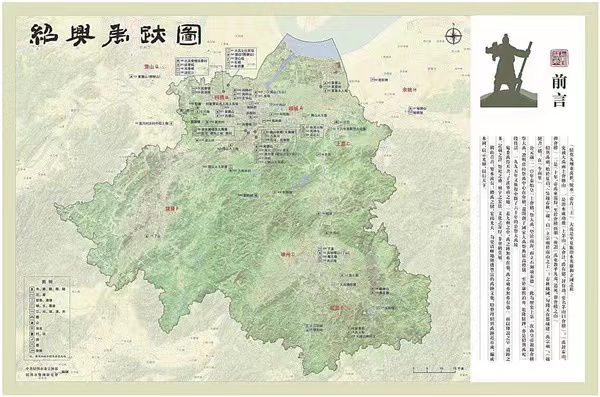
Map of Traces of Yu in the city of Shaoxing in Zhejiang province. [Photo provided to China Daily]
In this time, it is said, his wife, eagerly awaiting his return month in and month out, could not help but utter in increasing frustration,"Oh, I am waiting for him." This single line, some experts say, is the first poem composed by a female writer in China.
"Yu is a cultural totem of perseverance and struggle for the Chinese nation in the face of difficulties," says Tan Xuming, head of the Water History Committee of the Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society.
Over time Yuji, or the traces of Yu, have become an integral part of society and culture. "They are a moral symbol to encourage the Chinese people to bravely fight natural disasters and work together in times of trouble," Tan says. "Yu and his stories serve as a spiritual bond that has linked the Chinese people throughout history."
They do more than connect Chinese people; they have a deep influence on other East Asian countries too, Japan and South Korea in particular, where many Yuji, or traces of Yu, can be found. For example, in Japan, more than 150 such traces have been documented.
With the publication of the Chinese version of the two maps of traces of Yu in Japan and South Korea on the same day as Zhongguo Yuji Tu, a map covering the whole of East Asia is expected to be published in the near future.
"As in China, the stories of Yu have taken deep root among Japanese and Koreans," says He Junjie, director of the Shaoxing Municipal Bureau of Culture and Tourism. "The ancient sage helped with flood control during his time, and now he is helping strengthen cultural exchanges between different nations."
If you have any further problems with this article, please contact us at app@chinadaily.com.cn and we'll immediately get back to you.


 Shaoxing Showdowns
Shaoxing Showdowns Zhejiang: A Decade of Progress
Zhejiang: A Decade of Progress Shaoxing in expats' eyes
Shaoxing in expats' eyes