Zhejiang villages make strides in digitalization
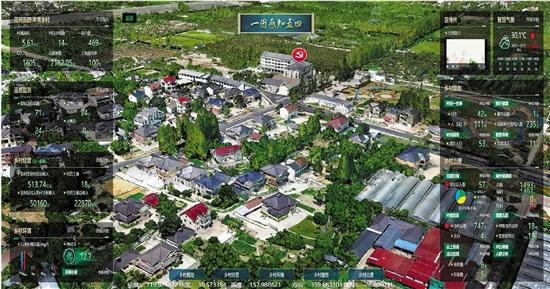
A digital map of a village in Deqing county, Zhejiang province, provides a massive amount of data in more than 230 categories. [Photo/zj.zjol.com.cn]
China's rural villages are rapidly embracing digital technologies. Internet of things technologies are being applied in agricultural production, agricultural products are being promoted through e-commerce platforms and commercial livestreams, and digital tools are being used in rural governance, to name just a few examples of how the technologies are being used.
The overall digitalization level in rural areas in East China's Zhejiang province is currently rated at 68.8 percent, which is 32.8 percentage points higher than the national average. Four Zhejiang localities, namely Hangzhou's Lin'an district, the cities of Cixi and Pinghu, and Deqing county, were recently listed among the first pilot zones in the national initiative to digitalize villages.
Digitalization has given rise to more detailed management practices in the province's villages.
Using a dedicated information system for agricultural supplies, farmers in Pinghu are able to purchase agricultural fertilizers and pesticides via mobile phones. Farmers enter the system via facial recognition and receive purchasing advice based on the records of their crops. Unadvised purchases are automatically banned in the system.
Villages in Hangzhou's Lin'an district launched a smart cloud platform to monitor garbage sorting in September. Garbage bins at each and every house in the district have been installed with chips which can identify which household an individual belongs to. Any garbage sorting misconduct will be traced back to the responsible household.
Using geographical information, artificial intelligence, and remote sensing, Deqing county has managed to make digital maps of its rural villages, allowing grassroots cadres to closely monitor the situation on the ground, greatly improving their administrative efficiency.

 Print
Print Mail
Mail
 20 Cultural Symbols
20 Cultural Symbols Why Zhejiang
Why Zhejiang Experiencing high-tech products at WIC
Experiencing high-tech products at WIC Zhejiang Release
Zhejiang Release Zhejiang News
Zhejiang News